AMIFICAS promotes and supports F-CAD to execute in-silico experiments, i.e. experiments, which can be fully performed on supercomputer facilities as a service for pharmaceutical companies, marketing, developing and manufacturing solid dosage forms such as tablets, hard gelatin capsules, pellets, granules, powder for inhalation etc.
The in-silico experiments include mixing, granulation, fluidized bed drying, tableting, coating, spray-freeze drying of liquids forming spherical particles with porosity up to 80% for inhalation purposes, etc. The In-silico experiments can be done for low or high dose, immediate and/or controlled release solid dosage forms including one or more active substances. For this purpose it is necessary to know the physic-chemical properties of the drug substance and the excipients used in the formulation including particle size distributions, real and bulk and tapped densities of the primary substances etc. F-CAD allows to perform a sensitivity analysis concerning the robustness of a formulation. Thus it is possible to calculate, how the drug release profile is affected by a change of the shape of the tablet, by a change of particle size distributions of the drug substances and/or the excipients, by a change in the concentration of the functional components etc
The advantages are the following:
- The connectivity between the company Departments Marketing, Research & Development and Manufacturing can be increased.
- The number of necessary lab experiments can be reduced substantially.
- Quality by Design becomes affordable in an early phase of development thanks to in-silico experiments and minimizing lab experiments.
- A robust solid dosage form ready for the market with different strengths can be provided already for Clinical Phase I Studies.
- F-CAD facilitates the definition of specifications for the primary substances used in the formulation.
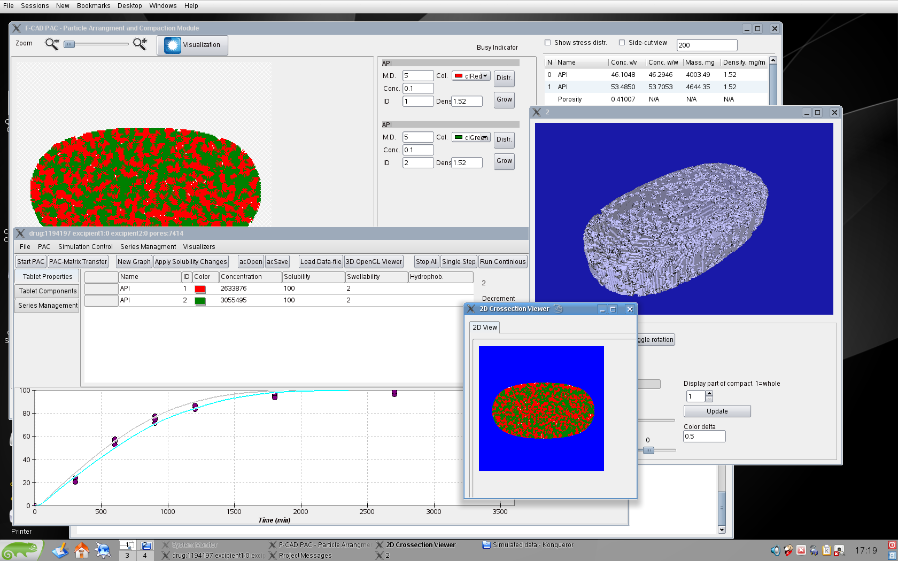
Figure 1. User interface of F-CAD main modules.

Figure 2. Using of computer-aided approach at earlier stages of
pharmaceutical development will remove unnecessary actions before
product launch.
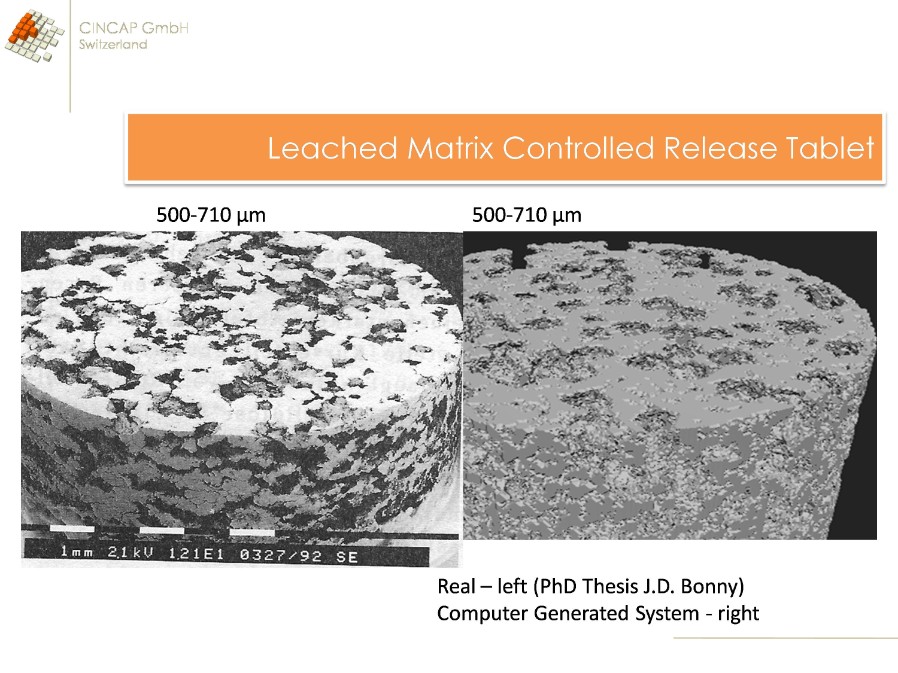
Figure 3. Realistic modeling of particle arrangement and compaction within pharmaceutical tablet.

Figure 4. Example of nanocomposite particle modeling using F-CAD.